Capture Technologies

Creating effective carbon capture solutions.
The EERC has decades of expertise and capabilities in carbon dioxide capture technologies. Over the last several years, we have mobilized our amine-based postcombustion capture system to conduct long-term capture studies at two lignite-fired power plants in North Dakota. These studies have provided critical validation of commercial solvent performance on actual flue gas to support the engineering design of full-scale capture plants. We have also investigated the potential for other carbon removal technologies including removing CO2 directly from ambient air and oceans.
Capture from Combustion
The EERC has conducted extensive pilot-scale testing of pre- and postcombustion carbon capture from the combustion and gasification of various biomass sources (e.g., crop and forestry residues) and biomass–coal blends. These studies elucidated the potential impacts of incorporating biomass fuels on carbon capture technologies that were originally developed for the fossil power industry. This approach is known as bioenergy with carbon capture and sequestration (BECCS) or biomass with carbon removal and storage (BiCRS).

Image courtesy of NETL Direct Air Capture Center
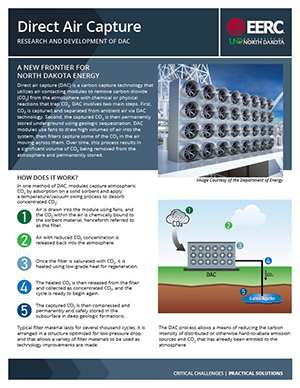
Direct Air Capture
Direct air capture (DAC) is a carbon capture technology that utilizes air-contacting modules to remove CO2 from the atmosphere with chemical or physical reactions that trap CO2. DAC involves two main steps. First, CO2 is captured and separated from ambient air using DAC technology. Second, the captured CO2 is then permanently stored underground using geologic sequestration. DAC modules use fans to draw high volumes of air into the system, then filters capture some of the CO2 in the air moving across them. Over time, this process results in a significant volume of CO2 being removed from the atmosphere and permanently stored.
North Dakota is an ideal location to develop DAC projects because of the state's long-standing experience with safely leveraging subsurface resources along with established and experienced service industries with the trained workforce necessary to support DAC projects. The EERC is supporting the development of a DAC hub by working with industry to develop carbon storage projects and to pursue opportunities to integrate DAC infrastructure through public–private partnerships such as the U.S. Department of Energy’s DAC Hub Initiative.
Yes. CO2 capture and transportation is safe and well-regulated and has been occurring in North Dakota for more than 20 years.
DAC facilities are relatively compact and consist mainly of fans that are shielded (much like a fan used at home) to protect wildlife. Facilities are generally less than 40 ft tall.
DAC technology uses low-carbon or zero-carbon energy to power their systems because the carbon produced from operating the DAC facility is deducted from the credits generated.
DAC plants can utilize waste heat for energy and, therefore, could partner with existing industrial facilities in the state for mutual benefit.
Not only does North Dakota have the ideal geology for safely capturing and storing CO2, but it also has the regulatory framework already set in place. DAC is one part of an all-of-the-above approach to a safe, resilient, reliable, economic, environmentally sustainable, and diversified economy.
DAC does not reduce local CO2 available for crop production. Unlike CO2 capture from a concentrated point source (i.e., power plant or ethanol facility), which is designed to capture nearly all CO2 within the stream, DAC is designed to remove 70%–90% of the CO2 from the air stream, but the diffusion of CO2 is rapid and does not change the local CO2 concentration.
CO2 mixes extremely quickly in the atmosphere—the concentration of CO2 in the air is roughly 420 ppm everywhere in the world. That means that if you remove a few ppm of CO2 from an air stream anywhere in the world, it is meaningful on a global perspective without creating a negative impact locally.
There is a commercial DAC facility in Iceland that is capturing and storing 4000 tonnes of CO2 per year.
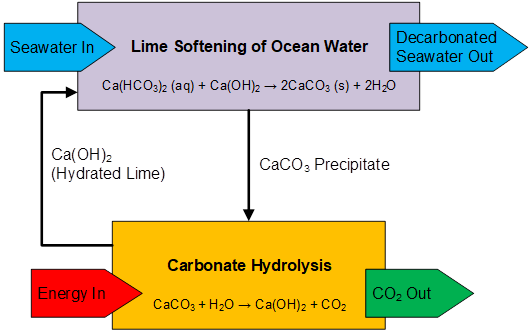
Hydrolytic Softening Concept for Direct Ocean Capture.
Direct Ocean Capture
The world’s oceans are estimated to have absorbed roughly one-third of the CO2 added to the atmosphere from human activities, lowering its pH by 0.1 units in the process. This accumulation affects the health of the oceans since CO2 acidification contributes to coral bleaching, and it hinders the growth of shell-forming marine animals.
Through prior research related to the treatment of oilfield produced water, the EERC has developed a novel direct ocean capture (DOC) process for marine carbon dioxide removal (mCDR) with support from the Advanced Research Projects Agency-Energy (ARPA-E). The technology is based on the cyclic precipitation of carbonates from ocean water in a process called hydrolytic softening, and it is projected to be one route for achieving the performance goals set forth in the U.S. Department of Energy’s Carbon Negative Shot.
Additional Resources