Carbon Storage
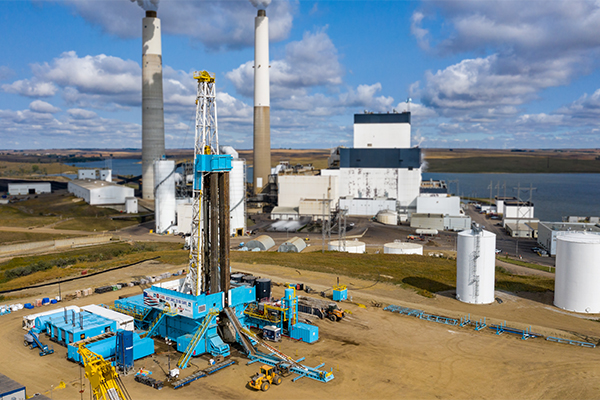

Safe and Permanent Carbon Storage
For over 20 years, the EERC has been a world leader in carbon storage, providing the foundational site characterization, laboratory analyses, modeling, simulation, and regulatory data upon which the CCS industry continues to build. Our work in carbon storage has been essential to understanding the challenges that face commercial-scale CCS and identifying solutions that contribute to the safe and successful operation of large-scale carbon storage projects. We have a long history working with project partners from around the globe to design, test, and deploy innovative CCS technologies.
Dedicated vs. Associated Storage
Carbon storage projects can be broadly divided into two types: dedicated storage and associated storage. The term “dedicated storage” refers to carbon storage in a dedicated geological reservoir, commonly a deep saline formation, where mitigation of CO2 emissions is the primary purpose of the underground injection. In contrast, “associated storage” refers to carbon storage where CO2 mitigation is a secondary aspect of the injection operations, typically at enhanced oil recovery sites (CO2 EOR).

The EERC is a world leader in dedicated storage projects, having led the detailed site characterization, laboratory analyses, modeling, simulation, and permitting work for the Red Trail Energy ethanol plant and two additional permitted storage facilities for Minnkota Power Cooperative's Milton R. Young Station. Several other announced projects will be pursuing carbon storage permits to manage emissions from existing ethanol plants and a coal-fired power plant. Through our unique positions with the PCOR Partnership, CarbonSAFE Initiative, and ongoing commercial CCS projects, the EERC continues to lead the fundamental technical work underlying carbon storage projects.
The EERC has the in-house expertise to support the entire carbon storage project life cycle. From site screening and feasibility stages through the design, operation, and close/postclosure phases, the EERC has the know-how and experience to navigate our clients through the process.
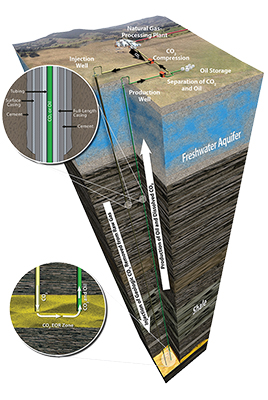
During the CO2 EOR process, large quantities of CO2 are injected to improve oil recovery and nearly all the CO2 (greater than 95%) is permanently stored in the reservoir during the process. Associated storage through CO2 EOR is sometimes called “CCUS,” or carbon capture, utilization, and storage, to denote that the injected CO2 is being utilized prior to storage and to distinguish the process from CCS (dedicated storage).
The EERC is actively involved in CO2 EOR projects for both conventional reservoirs (more porous formations) and unconventional reservoirs (tight formations, most notably the Bakken petroleum system, or “Bakken,” in western North Dakota).
Monitoring and Verification
As required by state and federal regulations, carbon storage project operators must monitor their sites to ensure protection of underground sources of drinking water (USDWs), human health, and the environment and to qualify for specific financial incentive programs. Monitoring requirements are specific to state and federal programs. Several monitoring technologies are used to acquire measurements from the different monitoring environments, which each provide complementary information about regulatory compliance and the safe operation of the site.
The EERC manages and executes studies ranging from pilot to commercial scale that demonstrate the improved cost efficiency and effectiveness of advanced monitoring and verification technologies that are low-impact, semiautonomous, continuous, and real-time. We are accelerating the commercial implementation of these technologies through the PCOR Partnership. In addition, the EERC actively works with the state of North Dakota through the State Energy Research Center (SERC) program to provide solutions to emerging topics critical to the state’s energy industry and environmental challenges, including recommending a statewide seismicity-monitoring network for fulfilling CCUS policy framework requirements.
Permitting and Regulatory
The EERC has a unique and successful track record of working with clients from across the energy industry and North Dakota’s underground injection control (UIC) Class VI permitting program authorities to permit commercial-scale CCS projects. As part of the permit application process, we work with our clients to generate testing and monitoring plans that comply with regulatory requirements, are protective of USDWs, and provide assurance of long-term containment of CO2 in the storage reservoir. In developing testing and monitoring plans, we work closely with the client and state regulatory authority to customize each monitoring plan to site-specific needs.



